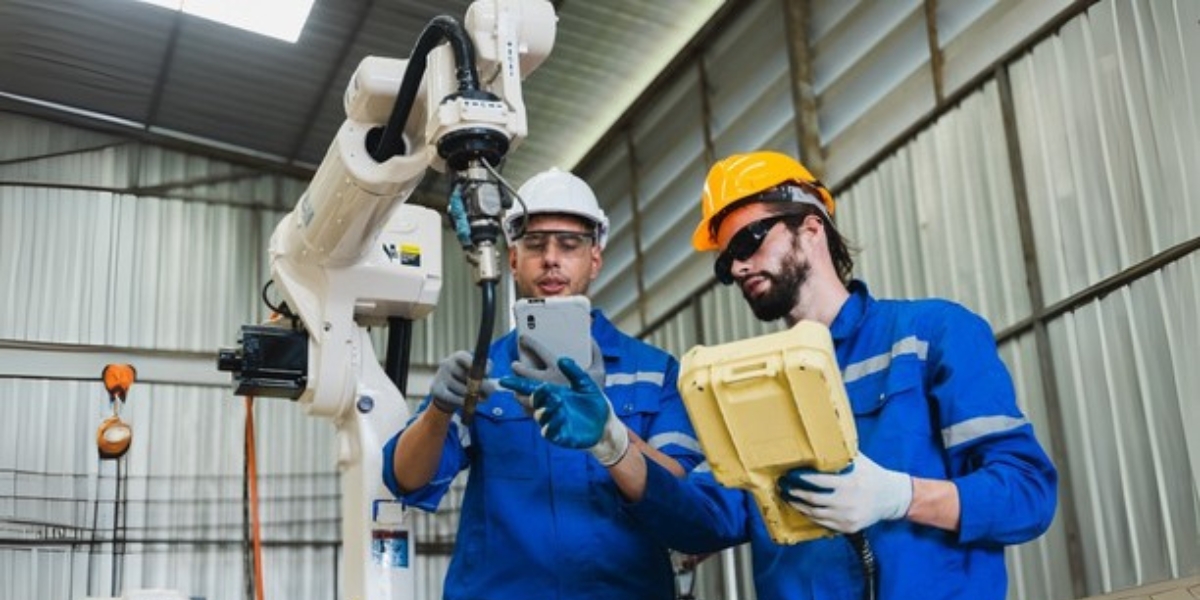
Exploring What an Automation Technician Does to Keep Systems Running
In industries where every second counts and operational efficiency is critical, automation has become the foundation of modern production. From assembly lines and packaging systems to robotics and precision-controlled environments, automated technology is everywhere. However, highly skilled professionals known as automation technicians are necessary to operate these intricate systems.
For businesses that depend on industrial machinery and control systems, having a clear understanding of the automation technician role is more than helpful it’s strategic. These professionals ensure equipment runs safely, efficiently, and with minimal downtime, ultimately protecting your productivity and bottom line. So, what exactly do they do, and why are they so vital to industrial success?
Let’s explore their key responsibilities and the value they bring to today’s automated environments.
Key Automation Technician Responsibilities: Keeping Industry Moving
In industrial environments where efficiency is everything, automation is the invisible engine powering daily operations. But like any engine, automation systems require constant oversight, adjustments, and care. This is where the automation technician comes in. While many ask, what does an automation technician do, the answer lies in a range of vital hands-on tasks and responsibilities that keep entire production lines functioning smoothly.
From installation to troubleshooting, automation technicians are essential to business continuity, safety, and operational excellence. This article dives deep into the automation technician responsibilities, showcasing why their role is indispensable across sectors.
1. Installation of Automation Equipment
At the heart of automation is the precise setup of components that work in perfect harmony sensors, relays, actuators, controllers, motors, and more. Automation technicians are responsible for installing these elements during system deployment or upgrades.
Installation requires much more than plugging devices into a system. It involves:
- Reading and interpreting wiring diagrams and blueprints
- Mounting devices and control panels securely
- Ensuring that components meet safety and industry compliance standards
- Wiring and connecting devices to control systems with accuracy
This phase lays the foundation for all automation processes that follow. A poorly executed installation can lead to costly breakdowns, inefficiencies, and long-term wear on equipment.
2. Programming and System Configuration
While automation engineers often handle the design and logic, technicians assist in programming devices such as Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs), Human Machine Interfaces (HMIs), and sensor networks. A technician may be required to:
- Upload or modify control programs
- Adjust system parameters
- Integrate newly added components
- Test response times and operational sequences
For companies using tailored production sequences, technicians ensure that the software aligns perfectly with mechanical processes. Their deep understanding of how software logic influences physical movement makes them crucial for seamless system behavior.
3. Preventive Maintenance
One of the most critical automation technician responsibilities is performing routine maintenance. Just like vehicles need regular servicing, automation systems require timely checks and adjustments to stay in top condition.
Preventive maintenance includes:
- Inspecting equipment for wear and tear
- Cleaning sensitive components
- Testing fail-safe systems and alarms
- Replacing aged or at-risk parts
- Logging maintenance records for audits and analysis
A consistent maintenance schedule minimizes unplanned downtime and significantly extends equipment life. Businesses that prioritize this service see fewer breakdowns and better long-term returns on automation investments.
4. Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
Machines don’t always behave as expected. When a system error occurs, production stalls, and money is lost with every passing minute. This is when the real value of a technician is realized.
A core part of the automation technician role is rapid and effective problem-solving. Using tools like multimeters, signal tracers, diagnostic software, and thermal cameras, technicians can quickly locate issues such as:
- Faulty wiring or connections
- Overheated components
- Software communication errors
- Sensor calibration mismatches
- Electrical shorts or overloads
Once identified, technicians either repair or replace the affected part and recalibrate the system restoring normal operation with minimal disruption.
5. Automation Repair and Replacement
In many cases, the fix involves more than tweaking software or restarting machines. Physical components wear out, break, or degrade over time. That’s where automation repair comes in another essential responsibility.
Repair duties may include:
- Replacing sensors, fuses, or relays
- Repairing wiring or connections
- Reassembling damaged control cabinets
- Installing refurbished modules or control units
- Testing repaired systems for safe operation
Companies like Horizon Elect Devices specialize in automation repair services, offering skilled technicians who can repair onsite or transport components for offsite refurbishment. Partnering with experts ensures fast, reliable service and reduces reliance on expensive equipment replacements.
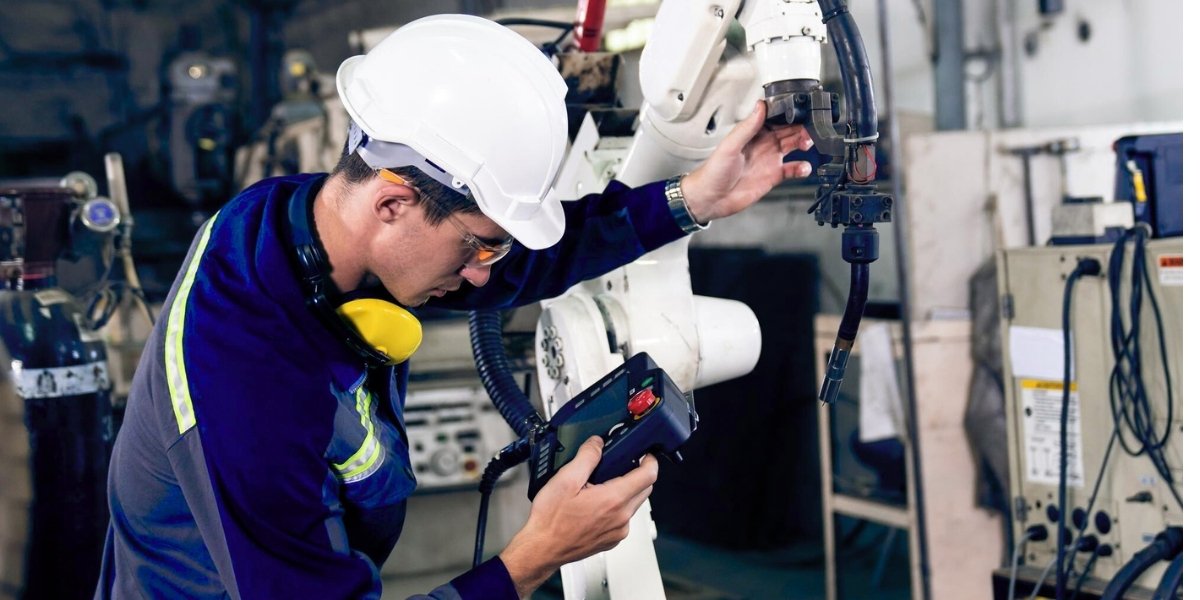

6. System Upgrades and Modifications
As industries evolve, so must the systems that drive them. Technicians play a central role in scaling operations by implementing upgrades or adjusting existing automation systems to new processes or technologies.
This could involve:
- Adding new devices or sensors to existing frameworks
- Installing upgraded control software
- Adjusting machine programming to handle new products or processes
- Improving efficiency through layout changes or faster communication protocols
The ability to retrofit and enhance automation without replacing the entire system makes automation technicians invaluable when growth or innovation is required.
7. Safety Assurance and Risk Mitigation
In industrial environments, automation isn’t just about efficiency it’s about safety. Machines must function within controlled limits to protect workers and infrastructure.
Automation technicians are tasked with:
- Testing emergency stop systems
- Verifying proper operation of safety interlocks
- Checking for potential shock or fire hazards
- Ensuring safe load levels and speeds
- Maintaining backup systems and power redundancy
By routinely validating these safety elements, technicians help companies avoid accidents, meet regulatory standards, and provide safer workplaces.
8. Support for Industrial Electronics Repair
Many automation systems include embedded electronic circuit boards, drivers, power modules, and control chips. These components fall under the domain of industrial electronics repair, another responsibility that overlaps with the technician’s role.
Technicians often:
- Diagnose faulty electronics using testing equipment
- Replace or recommend replacement of damaged PCBs or modules
- Coordinate with specialized repair labs for advanced fixes
- Ensure repaired parts are calibrated and reintegrated into the system
For companies in regions like the UAE, accessing reliable industrial electronics repair services is critical. Having trained technicians on your team or through partners like Horizon Elect Devices means faster repairs and less downtime.
9. Documentation and Reporting
Every inspection, repair, and upgrade must be logged. Accurate documentation helps with audits, future repairs, and identifying recurring issues.
Automation technicians are responsible for:
- Maintaining service logs and maintenance schedules
- Recording part replacements and firmware updates
- Noting compliance checks and safety verifications
- Reporting equipment usage statistics and performance anomalies
Well-maintained records provide insights into equipment longevity and help predict future maintenance needs.
Powering Efficiency Through Skilled Technical Support
So, when people ask what does an automation technician do, the full answer lies in these responsibilities: installing, configuring, maintaining, repairing, upgrading, and protecting complex automated systems. Their expertise keeps operations running, ensures worker safety, and extends the life of high-value industrial equipment.
Whether you’re setting up a new plant or keeping an existing one at peak performance, having a skilled technician or partnering with trusted industrial electronics repair service providers like Horizon Elect Devices can make all the difference.
These professionals are more than just troubleshooters; they’re the backbone of modern industry.